Begin with the lowest effective dose: Typically, this is 25-50mg for oral sumatriptan and 6mg for the subcutaneous injection. Adjust upwards only if needed and under medical supervision.
Oral sumatriptan tablets are usually taken at the first sign of a migraine. Remember, you shouldn’t exceed 100mg in a 24-hour period. If your symptoms don’t improve after taking the first dose, wait at least two hours before considering a second dose, but do not exceed the maximum daily dose.
Subcutaneous sumatriptan offers a faster onset of action. Follow your doctor’s specific instructions on administration and dosage. It’s crucial to understand that this route isn’t suitable for everyone, and your physician will assess your suitability.
Important Note: Sumatriptan is not a preventative medication. It’s designed to relieve migraine symptoms *after* they begin. Discuss preventative strategies with your doctor if you experience frequent migraines.
Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any new medication, including sumatriptan, and especially before adjusting your dose. They can provide personalized guidance based on your medical history and individual needs.
- Sumatriptan Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
- Oral Sumatriptan
- Nasal Spray Sumatriptan
- Subcutaneous Injection Sumatriptan
- Important Considerations
- Contraindications
- Understanding Sumatriptan: What it is and how it works
- Standard Sumatriptan Dosage for Migraine Relief
- Oral Sumatriptan Dosage Guidelines
- Nasal Spray Dosage Guidelines
- Dosage Adjustments Based on Patient Factors (Age, Liver/Kidney Function)
- Hepatic Impairment
- Renal Impairment
- Further Advice
- Sumatriptan Dosage Forms: Oral, Nasal Spray, Injection
- Oral Sumatriptan
- Nasal Spray Sumatriptan
- Injectable Sumatriptan
- Frequency of Sumatriptan Use: Avoiding Overuse Headaches
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions with Other Medications
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Sumatriptan Dosage
- Dosage Adjustments and Medication Interactions
- Frequency and Severity of Migraines
Sumatriptan Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
Sumatriptan comes in various forms: oral tablets (25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg), nasal spray (20 mg), and subcutaneous injection (6 mg). Dosage depends on the formulation and your individual needs. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Oral Sumatriptan
For oral tablets, the typical starting dose is 25-50 mg. You may take a second dose after two hours if needed, but do not exceed 100 mg in a 24-hour period. If you’ve had a prior migraine, your doctor may prescribe a higher starting dose. Note that some individuals may experience side effects such as nausea or dizziness.
Nasal Spray Sumatriptan
The nasal spray delivers 20 mg per dose. This is typically a single dose; repeat administration within 24 hours should only be done under strict medical supervision. Keep in mind that nasal congestion can impact absorption.
Subcutaneous Injection Sumatriptan
The subcutaneous injection delivers 6 mg. This is usually a single dose; avoid multiple injections without a doctor’s approval. Proper injection technique is crucial for efficacy and to minimize discomfort.
Important Considerations
Factors influencing dosage include your migraine history, response to previous treatments, and other medications you’re taking. Always inform your doctor about all your health conditions and medications. Do not exceed the maximum recommended daily dose. If your migraines are not effectively managed, consult your doctor to discuss alternative treatment options. Avoid overuse, as this can lead to medication overuse headache.
Contraindications
Sumatriptan is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain heart conditions, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or a history of stroke should avoid it. Your doctor will assess your suitability before prescribing.
Understanding Sumatriptan: What it is and how it works
Sumatriptan is a triptan, a class of medication specifically designed to treat migraine headaches. It works by narrowing blood vessels in the brain, which are thought to contribute to migraine pain. This action helps reduce the throbbing pain and other migraine symptoms.
Sumatriptan also affects the release of certain chemicals in the brain, including serotonin. This neurotransmitter plays a role in pain signaling, and by influencing its release, sumatriptan helps alleviate migraine pain and associated nausea.
Different forms of sumatriptan exist, including tablets, nasal sprays, and injections. Your doctor will recommend the best form based on your needs and preferences. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and administration.
While sumatriptan provides effective relief for many, it’s not suitable for everyone. It’s crucial to discuss potential side effects with your physician. Common side effects can include dizziness, tingling sensations, and drowsiness. In rare cases, more serious side effects may occur.
Remember, sumatriptan is a medication for treating acute migraine attacks, not for migraine prevention. For preventing migraines, other medications are necessary.
Standard Sumatriptan Dosage for Migraine Relief
Sumatriptan comes in various forms, affecting dosage recommendations. Oral tablets typically range from 25mg to 100mg, with a common starting dose of 50mg. You can take a second dose after two hours if needed, but do not exceed 100mg within a 24-hour period.
Oral Sumatriptan Dosage Guidelines
- Initial Dose: Usually 50mg.
- Second Dose (if needed): 50mg after at least two hours. Do not exceed 100mg in 24 hours.
- Maximum Daily Dose: 100mg.
Nasal spray formulations usually contain 5mg or 20mg per spray. The typical dose is one spray (5-20mg), with a potential for a second spray after one hour if needed, but again, respecting the maximum daily dose.
Nasal Spray Dosage Guidelines
- Initial Dose: One spray (5mg or 20mg, depending on the formulation).
- Second Dose (if needed): One spray (5mg or 20mg) after at least one hour. Check the maximum daily dose on your specific medication.
Injectable sumatriptan typically uses a 6mg dose. This form is usually administered by a healthcare professional. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
- Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting sumatriptan or adjusting your dosage. They can help determine the best approach based on your medical history and individual needs.
- Do not exceed the recommended maximum daily dose. Overdosing can lead to adverse effects.
- Be aware of potential side effects and seek medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Dosage Adjustments Based on Patient Factors (Age, Liver/Kidney Function)
Sumatriptan dosage rarely requires modification based solely on age in adults. However, considerations for hepatic and renal impairment are paramount.
Hepatic Impairment
For patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C), reduce the initial sumatriptan dose by 50%. Closely monitor for adverse effects. A lower maintenance dose might also be necessary.
Renal Impairment
Sumatriptan is primarily metabolized by the liver, and renal excretion of unchanged drug is minimal. Therefore, dosage adjustments for mild to moderate renal impairment are usually not needed. However, for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min), consult product labeling for specific guidance; dose reduction might be considered, though evidence supporting specific adjustments is limited. Close monitoring is vital in all cases of renal dysfunction.
Further Advice
Always consult current prescribing information and consider individual patient factors. Patient response to sumatriptan varies. Regularly assess the patient’s response to treatment and adjust accordingly, under medical supervision. These are general guidelines; individual patient needs should always be prioritized.
Sumatriptan Dosage Forms: Oral, Nasal Spray, Injection
Sumatriptan is available in several forms, each with its own administration method and dosage guidelines. Choosing the right form depends on individual needs and physician recommendations. Let’s explore the options:
Oral Sumatriptan
Oral sumatriptan comes in tablets and can be a convenient option. Typical dosages range from 25mg to 100mg, with a maximum daily dose usually not exceeding 300mg. Always follow your doctor’s instructions for frequency and timing of doses.
Nasal Spray Sumatriptan
Nasal spray offers faster absorption compared to oral forms. Common dosages are 5mg or 10mg per spray, usually administered as a single dose per migraine episode. Do not exceed the recommended dosage. Read the accompanying instructions carefully before use.
Injectable Sumatriptan
Injectable sumatriptan offers the quickest relief. This form is typically administered by a healthcare professional and dosages vary. Common dosages include 6mg subcutaneously (under the skin). You should only receive injections from a qualified medical professional.
Important Note: This information is for general knowledge only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized dosage recommendations, potential side effects, and drug interactions before using sumatriptan.
- Remember: Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on individual factors and response to treatment.
- Caution: Sumatriptan is not suitable for everyone. Discuss any pre-existing health conditions with your doctor.
- Storage: Store sumatriptan as directed on the packaging to maintain its effectiveness.
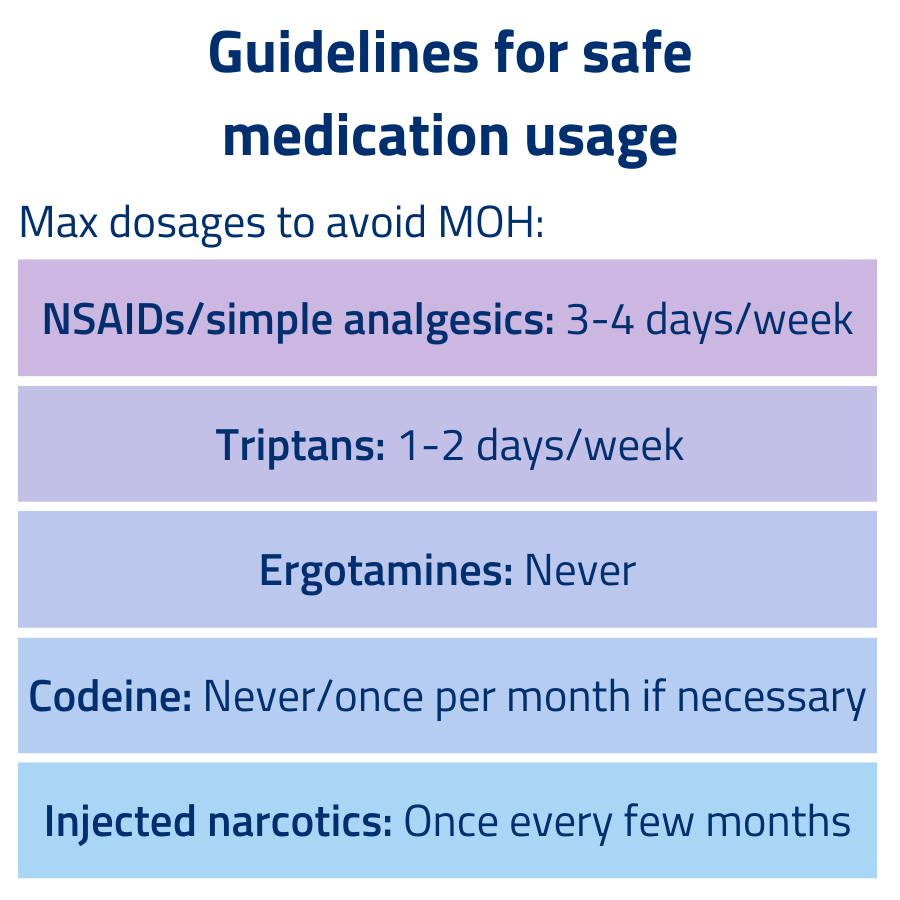
Frequency of Sumatriptan Use: Avoiding Overuse Headaches
Don’t exceed two sumatriptan doses within a 24-hour period. This helps prevent medication overuse headaches.
Aim for no more than nine to ten sumatriptan doses per month. Consistent overuse can lead to daily headaches.
If you frequently need sumatriptan, discuss preventative treatments with your doctor. Options include daily medications or lifestyle changes.
Keep a headache diary. Tracking headache frequency and severity, along with sumatriptan use, helps your doctor assess your treatment plan’s efficacy.
Recognize the signs of medication overuse headache. These often present as daily headaches that worsen with sumatriptan use.
Consider alternative treatments for migraines when possible. These can include stress management techniques, proper hydration, and regular sleep.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. They can tailor your sumatriptan dosage and frequency based on your individual needs and medical history. Ignoring this advice can be harmful.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions with Other Medications
Sumatriptan, while effective for migraine relief, can cause side effects. Common ones include tingling sensations, warmth, pressure sensations, and dizziness. Less frequent but more serious side effects might include chest tightness, irregular heartbeat, or seizures. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Certain medications interact negatively with sumatriptan. MAO inhibitors, ergotamine-containing drugs, and other triptans should be avoided due to increased risk of serious cardiovascular events. Discuss all your current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, with your doctor before starting sumatriptan to prevent potential interactions.
Specifically, combining sumatriptan with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) can lead to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. Your doctor will assess your risk and advise accordingly.
Alcohol consumption can worsen sumatriptan’s side effects, particularly those affecting the cardiovascular system. Limit or avoid alcohol while taking this medication.
Always consult your physician or pharmacist for personalized advice on managing potential side effects and interactions, considering your individual health status and medication history.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Sumatriptan Dosage
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or any signs of a heart attack after taking sumatriptan. This is a serious side effect requiring immediate medical attention.
Also, seek medical advice if your migraine symptoms don’t improve or worsen after taking two doses of sumatriptan within 24 hours. This suggests the medication may not be effective enough, or your migraines might stem from an underlying condition.
Dosage Adjustments and Medication Interactions
Schedule a doctor’s appointment to discuss dosage adjustments if you find the current dosage ineffective or if you experience persistent side effects, like nausea or dizziness. Your doctor can help determine the optimal dosage and address potential side effect management strategies.
It’s vital to inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Some medications interact with sumatriptan, potentially causing adverse effects. Your doctor can assess potential drug interactions and make appropriate adjustments to your treatment plan.
Frequency and Severity of Migraines
Regularly discuss the frequency and severity of your migraines with your doctor. Changes in migraine patterns might necessitate a review of your sumatriptan treatment plan. Your doctor may consider alternative medications or treatment strategies based on your individual needs.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Chest pain, shortness of breath | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Migraine doesn’t improve after two doses | Consult your doctor |
| Persistent side effects | Discuss dosage adjustments with your doctor |
| Changes in migraine frequency or severity | Discuss with your doctor |
| New medication or supplement | Inform your doctor |